|
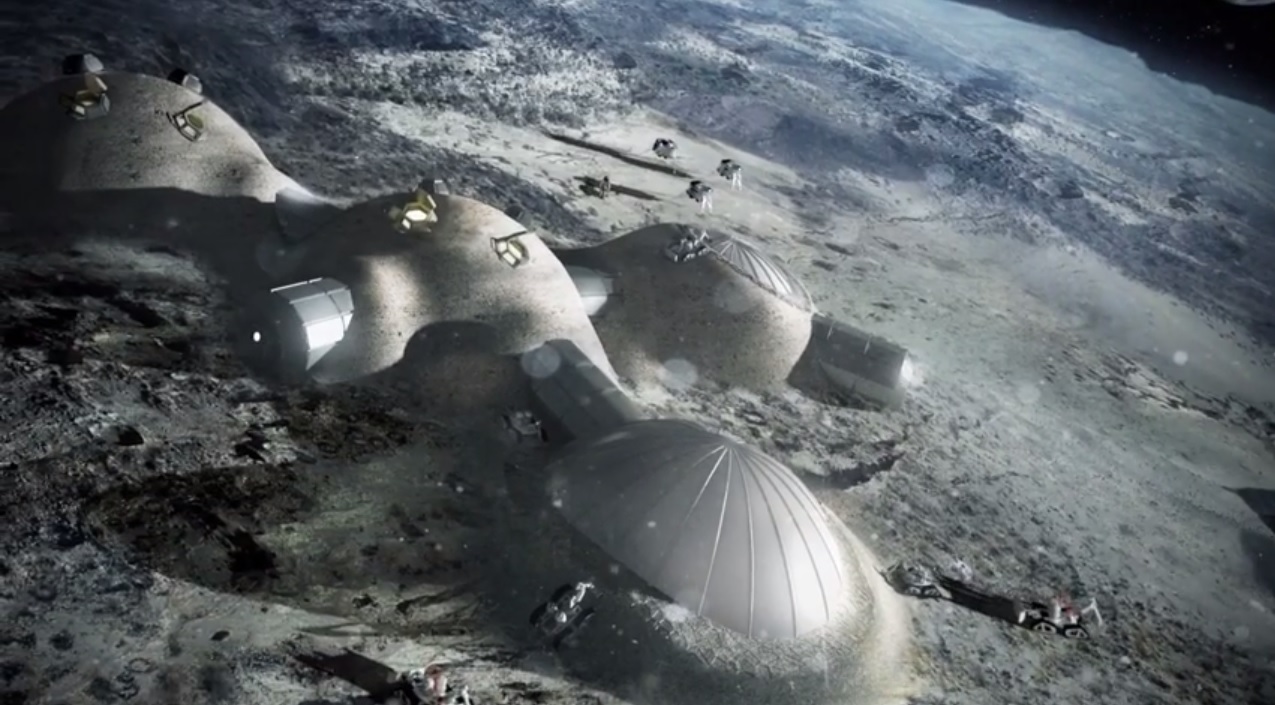
| The discovery of lunar caves could pave the way for long-term human habitats on the moon, indicating that an actual moon village could soon become a realityESA |
Human colonization of the
moon has long been a dream for space enthusiasts. However, the dream may now be
closer than ever to being realized, thanks to scientists having discovered an
ideal location for what could become a future moon base. Scientists have
confirmed the existence of a giant open lava tube.
This lava tube exists in the
Marius Hills region of the moon, which could potentially be used to protect
humans on the moon from the harsh atmospheric conditions on a long-term basis.
Since the moon, unlike the Earth, has extreme temperature variations, meteorite
impacts and even radiation, the only safe place for humans would be inside an
intact lava tube, according to a new study published in Geophysical Research
Letters.
Scientists from Japan's
space agency JAXA and Perdue University in the US used radar data from the
SELENE spacecraft to track suspected depressions on the moon's surface. They
found a large open lava tube. Although the presence of lava tubes on the moon has
been speculated in the past, the radar data used in the new study provides the
clearest picture yet of how big they are and what they look like.
"It's important to know
where and how big lunar lava tubes are if we're ever going to construct a lunar
base," Junichi Haruyama, a senior researcher at Jaxa, said in a statement.
"But knowing these things is also important for basic science. We might
get new types of rock samples, heat flow data and lunar quake observation
data."
Lunar Lava tubes are similar
to the ones found on Earth, but they are much bigger in size. They are
naturally occurring channels that are formed when molten lava quickly cools on
the outside while remaining hot and liquid-like within. Once the internal
stream of steaming lava stops flowing, it sometimes drains, forming a hollow
tunnel.
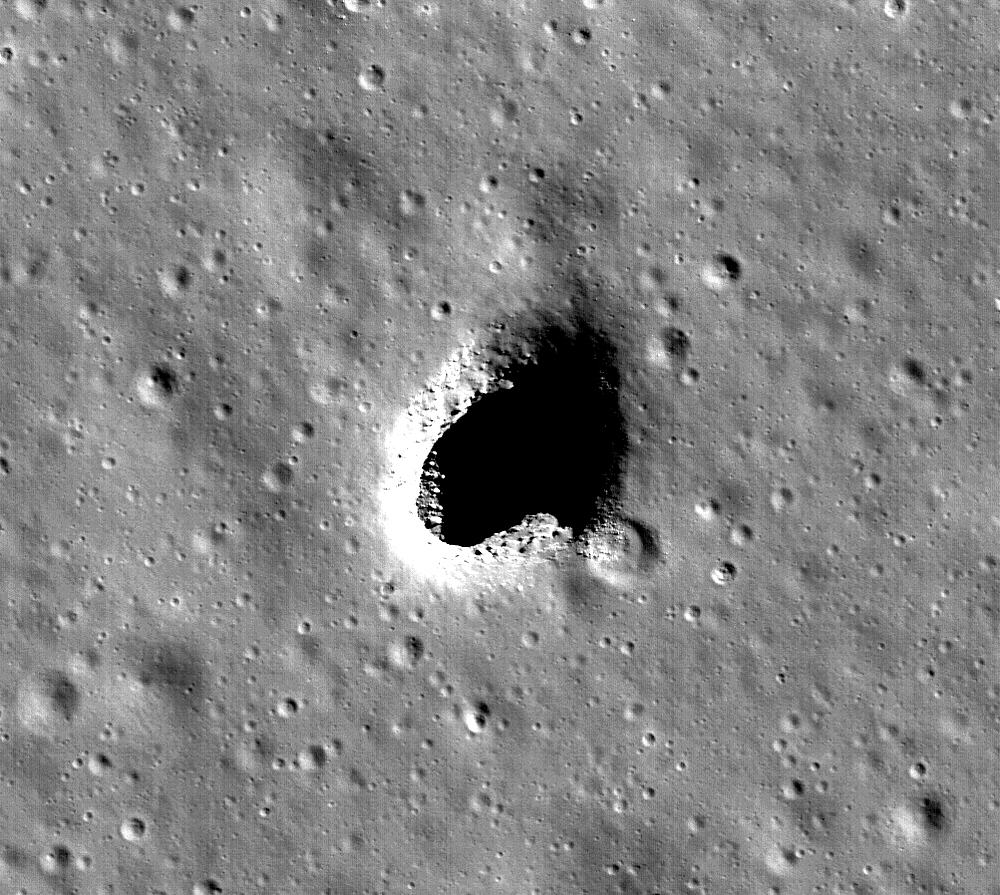 |
| The Marius Hills Skylight, as observed by the Japanese SELENE/Kaguya research teamNASA/Goddard/Arizona State University |
Apart from the Marius Hills
region, scientists have also recently found some similar patterns. These
patterns indicate the current presence of lava tubes in several other areas of
the moon. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) scientists also enlisted
the assistance of some scientists from NASA’s GRAIL mission, which involved
obtaining very high-quality data of the moon's gravitational field. The team
surveyed the areas on the moon where NASA’s GRAIL had spotted mass deficits.
"They knew about the
skylight in the Marius Hills, but they didn't have any idea how far that
underground cavity might have gone," said Jay Melosh, a GRAIL
co-investigator and Distinguished Professor of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary
Sciences at Purdue University. "Our group at Purdue used the gravity data
over that area to infer that the opening was part of a larger system. By using
this complimentary technique of radar, they were able to figure out how deep
and high the cavities are."
The longest duration that an
astronaut has spent on the moon till date is three days. This is primarily
because current space suits cannot withstand the harsh conditions on the lunar
surface for longer periods. However, the discovery of lunar caves could pave
the way for long-term human habitats on the moon, indicating that an actual
moon village could become a reality in the not-too-distant future.