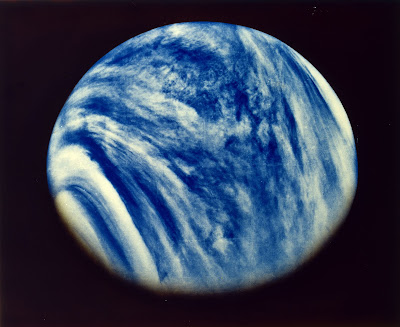
Venus is our closest planetary neighbor, and above its oppressive surface, in the clouds, there is a mystery. In the planet's clouds, scientists have discovered traces of phosphine, a substance that may be produced by living organisms.
In Venus' hazy atmosphere, life may exist, as scientists have long assumed. The surface of Venus reaches temperatures of more than 800 degrees Fahrenheit, making it unfriendly. No probe sent to the planet has managed to survive for more than a few hours. But the planet's atmosphere, which is made up of thick layers of sulfuric acid clouds, might offer a special environment for the development of new lifeforms.
“We know that the molecule phosphine is a biomarker on Earth,” astronomer Jane Greave, of Cardiff University in Wales, said in a pre-recorded statement released by the Royal Astronomical Society. “It’s been suggested that there are possible habitats in the cloud decks of Venus, so somewhere where little lifeforms could live.”
Fair enough, this most recent discovery does not specifically point to the existence of life on other planets, but it is the closest thing we've ever come. The only explanations for the molecule, according to the researchers, are that it is either being produced by a living entity or that it was created by a chemical process that is currently unknown to science. They published their findings in the journals Nature Astronomy and Astrobiology today.
Molecular of the Day
Phosphine (PH3) is made up of a single phosphorus atom sandwiched by three hydrogen atoms. “I like to think of phosphine as ammonia’s evil cousin,” Greaves said. (Ammonia, by comparison, is made up of a nitrogen atom surrounded by three hydrogen atoms.)
Anaerobic microbes, which thrive in environments without oxygen here on Earth, also produce phosphine. “They’ve got a completely different way of life to much of what we’re used to,” Greaves said.
Scientists have yet to determine how these microbes produce the compound, which can also be produced in a laboratory. Phosphine is poisonous to many animals, and the colorless, flammable gas has been used in chemical warfare and by farmers to snuff out tenacious pests.
The chemical has also been discovered elsewhere in the solar system, in the cores of Jupiter and Saturn. But, unlike Venus, there is a reason. The stifling heat and crushing pressure on these planets is strong enough to shatter hydrogen and phosphorus atoms together. However, there isn’t enough heat or pressure on Venus for phosphine to be produced this way.
Conditions aren’t so bad 31 miles above the Venusian surface. Temperatures linger at about 86 degrees Fahrenheit well above the rocky planet’s cloud decks. At this altitude, the air pressure is comparable to that found on Earth’s surface. The only catch is that Venus’s clouds are sulfuric alkaline, creating an extremely caustic environment.
However, in other cases, life on Earth flourishes under these conditions. Microbes have been identified in rocky crevices deep beneath the oceans and around geothermal springs in areas like Yellowstone and Iceland. The microorganisms that create phosphine have been found in the stomachs of animals such as penguins, deep sea worms, and, yes, humans.
The Mysterious Molecule: Surveillance
In order to identify the chemical makeup of distant atmospheres, scientists use radio telescopes to make observations across a wide swath of wavelengths of light. Greaves and her colleagues studied compounds in Venus’ deadly atmosphere using the James Clark Maxwell radio telescope atop Hawaii’s Mauna Kea volcano in 2017.
“If you look at a very specific wavelength, a little bit of that light is missing because the phosphine molecules have absorbed and so it’s not present,” Greaves said.
Greaves contacted MIT researchers after finding phosphine’s signature, and the two collaborated to make additional observations in 2019 using Chile’s Atacama Large Millimeter Array. The scientists would have made additional observations if the new coronavirus epidemic had not arrived earlier this year and largely shut down the world’s observatories.
According to National Geographic, the researchers was eventually able to define a range of altitudes, between 32 and 37 miles above the surface, where the molecule was abundant. And it was abundant, indeed: The scientists discovered concentrations of phosphine ranging between 5 to 20 parts per billion—way more than the amount in Earth’s atmosphere, and way more than the team expected to find.
Having phosphine dreams
Some experts are doubtful about the findings, speculating that there was an error in the data collection process.
“They took the right steps to verify the signal, but I’m still not convinced that this is real,” ALMA observatory scientist John Carpenter told National Geographic. “If it’s real, it’s a very cool result, but it needs follow-up to make it really convincing.” Other researchers chalk the findings up to some sort of undiscovered geochemical process.
That life could survive in the caustic clouds of Venus isn’t a new idea.
“The conditions in the lower clouds of Venus resemble those on Earth more than any other extraterrestrial environment now known,” astronomers Harold Morowitz and Carl Sagan wrote in the journal Nature in 1967. Despite Venus’s promise as a cradle for life, the planet has been largely ignored, either due to the logistical obstacles of getting there, or perhaps because other locations in the solar system—look at you, Mars and Europa—seemed more appealing.
NASA’s Mariner 2 became the first spacecraft to sail by Venus in 1962. The Soviet Union responded by sending its Venera spacecraft to the planet. The Venera 7 spacecraft was the first to survive a soft landing on Venus, although it melted within seconds. Venera 9 took the first image of the Venusian surface.
NASA’s Magellan mission launched in 1989, producing the first global map of Venus. Only the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency’s Akatsuki orbiter is currently monitoring Venus. Mars, by comparison, has eight active missions.
However, NASA is now considering two potential Discovery Program missions to Venus. VERITAS (Venus Emissivity, Radio Science, InSAR, Topography, and Spectroscopy) is one project that aims to scan the planet’s surface in order to uncover its many geologic secrets.
DAVINCI+, the other mission, intends to study Venus’s atmosphere by sending a probe down to the planet’s rocky surface. On the journey down, it will collect trace gas samples and take photographs of both the volatile atmosphere and the rocky surface below.
“Venus is the key to understanding how Earth-size planets evolve,” Martha Gilmore, an astronomer at Wesleyan University and a co-developer of both projects, said in a February press statement. “Like Earth, we predict Venus had an ocean that may have lasted for billions of years. Like Earth, Venus may be volcanically and tectonically active today.”
The two missions “will target the modern and ancient history of Venus, as recorded in the rocks and the atmosphere,” Gilmore said. While Mars has been in the spotlight for decades, Venus’s moment may not be far behind.
The Indian Space Research Organization declared plans to launch a mission to Venus in the coming years. Meanwhile, Rocket Lab CEO Peter Beck has spoken openly about his company’s plans to send a private research expedition to Venus.
“The biggest question that I can possibly think of to try and and answer is: Is life on Earth unique or is prolific throughout the universe?” Beck said in an interview on the Orbital Mechanics podcast. “If you could find life in the clouds of Venus, then you would gravitate to the natural assumption that actually life is prolific.”
Reference(s): National Geographic and Nature.

"The only explanations for the molecule, according to the researchers, are that it is either being produced by a living entity or that it was created by a chemical process that is currently unknown to science."
ReplyDeleteOn a different planet, with so different conditions (temperatures, pressures), the probability of discovering "a chemical process that is currently unknown to science" is much higher than discovering life.
How many thousands (or millions?) of articles need to be written about life that is not eventually found? It will be found one day and when it is, it will make sense to write about it but so many speculative articles are becoming so boring, uninteresting and irrelevant.
Would it not be more useful talking about the benefits of developing a space economy, and present discoveries that will allow humanity to utilise space and further improve conditions and our life on earth?
It’s life Jim but not as we know it.
ReplyDelete